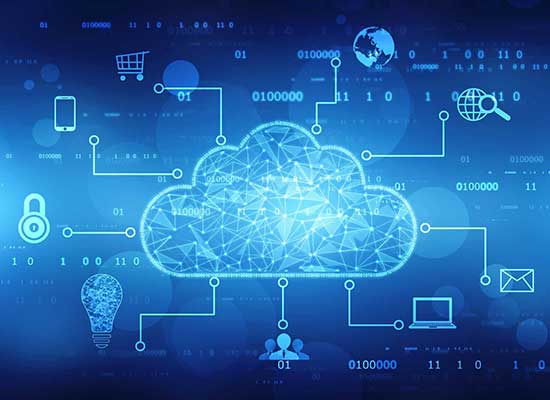
What is IoT?
IoT stands for ‘Internet of Things’.
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is a network of all objects (computers, mechanical devices, digital devices, animals, humans, and so on) with unique IDs and the capacity to transport data via a common network utilizing the internet. IoT needs no human-human or human-computer interaction.
The IoT network is a massive network of connected devices. In any physical unit, sensors are embedded; these can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, an automobile with built-in sensors to alert the driver when tire pressure is low, or any other natural or man-made object that can be assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address and can transfer data over a network are all examples of things in the internet of things.
How does IoT work?
An IoT ecosystem is made up of web-enabled smart devices that gather, transmit, and act on data from their surroundings using embedded systems such as CPUs, sensors, and communication hardware. By connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device, IoT devices may exchange sensor data that is either routed to the cloud for analysis or examined locally. These gadgets may sometimes interact with one another and act on the information they receive. Although individuals may engage with the devices to set them up, give them instructions, or retrieve data, the gadgets conduct most of the work without human participation.
Why is IoT important?
IoT has emerged as one of the most significant technologies of the twenty-first century in recent years. Now that we can link common items to the internet through embedded devices, including kitchen appliances, vehicles, thermostats, and baby monitors, seamless communication between people, processes, and things is conceivable.
Physical objects can exchange and gather data with minimum human interaction thanks to low-cost computers, the cloud, big data, analytics, and mobile technologies. Digital systems can record, monitor, and alter each interaction between linked items in today’s hyperconnected environment. The physical and digital worlds collide, yet they work together.
The advantages and disadvantages of IoT
The following are some of the benefits of IoT:
- Access information from anywhere at any time on any device.
- Minimizes human work and effort.
- Saves time and effort.
- Good for personal safety and security.
- Useful in traffic and other tracking or monitoring systems.
- Beneficial for the healthcare industry.
- Improved security in homes and offices.
- Reduced use of many electronic devices as one device does the job of a lot of other devices.
The following are some of IoT’s drawbacks:
- As the number of linked devices grows and more information is exchanged between them, the risk of a hacker stealing personal data grows as well.
- Increased unemployment rates.
- Highly dependent on the internet.
- Lack of mental and physical activity by humans leading to health issues.
- Complex system for maintenance.
Applications of IoT:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is commonly considered to be the beginning of the next industrial revolution. Because of technology improvements, physical things may now be incorporated into a single digital world. The number of IoT applications will increase as technology advances in the next years. IoT is expected to be used for Artificial Intelligence in the future to provide smart solutions. The following are some notable examples of IoT applications in the real world:
Smart City: The concept of a “Smart City” deals with the dynamic and long-term planning and management of a city through the transformation of services. Smart cities regulate government facilities, transportation and traffic control, power, health care, water, innovative urban gardening, trash management, and many other aspects of the territory through automation. Smart City IoT technologies help to alleviate traffic congestion, as well as minimize noise and pollutants. Municipal trash management that is intelligent offers the public with vital information that makes garbage management easier and more ecologically friendly. IoT technology also assists in solving a variety of city-related challenges, such as traffic, reducing air and noise pollution, and making communities more livable.
Smart Home: Controlling room lights, fans, TVs, and other electrical appliances remotely, controlling the home door, and remotely monitoring CCTV cameras are examples of smart home applications. We may also use IoT to monitor health problems, room temperature, humidity, and other factors. Overall, by implementing IoT, it is possible to automate every aspect of any room, which can then be controlled and monitored remotely.
Healthcare: IoT has diverse healthcare applications. IoT in healthcare brings new instruments updated with the latest technologies in the environment that aims to create improved healthcare facilities. Fitness trackers, for example, aid in the monitoring of a user’s daily activities such as sleep cycles, heart rate, exercise levels, fitness figures, burnt calories, and so on. IoT with machine learning applications which can open new endeavors in the health care sector.
Wearables: Wearables have become a hot topic for IoT applications in the future. Wearable devices can be used in smart homes to get health updates, receive phone calls, and SMS notifications, and dial or receive phone calls. Some wearable devices also have step counters and MP3 operations. As a result, wearable devices are an excellent IoT application.
Smart Car: Automobiles have gotten more viable, scalable, and quicker as technology has advanced. Central computers are installed in the automobile to collect data from sensors installed in various automotive components to assess engine oil level, radiator water temperature, and so on. The manufacturer can send the vehicle owner an email with information on the vehicle, or the vehicle owner can follow the state of the vehicle using an app put on their phone. All of this happens just because of IoT.
Smart Farming: Smart farming is an IoT application that is often overlooked. Farmers may utilize smart IoT farming apps to maximize a variety of tasks, such as determining the ideal time to harvest crops, creating soil chemistry-based fertilizer profiles, and monitoring soil nutrients and moisture concentrations. In agriculture, a number of sensors, such as animal-connected sensors, can help with livestock monitoring. For example, a microchip is implanted in the ox’s ear to track the animal’s health and, among other things, to record its vaccination history. Smart farming will become a major application area in nations that rely heavily on agricultural exports.
Industrial Internet: The Industrial Internet, often known as the Industrial Internet of Things, has become a buzzword in the automotive industry (IoT). With sensors, software, and big data analytics, it enables industrial innovation to create brilliant gadgets. The Internet of Things (IoT) has a lot of potential for quality control and long-term sustainability. The supply chain’s dependability might be improved by monitoring orders, exchanging real-time inventory information between manufacturers and merchants, and automating delivery. It also takes advantage of situations in which unforeseen interruptions and system breakdowns might result in life-threatening situations. According to General Electric an increase in corporate competitiveness will result in $10 trillion to $15 trillion in global GDP in the next 15 years.